- (888) 947-5273
- Mon-Sat 10m - 5pm
Information Technology is the use of digital technology, such as computers, smart phones and the internet to store & process data into useful information. While the entire scope of IT is vast, one of the most important elements is the impact the user has on the technology in use. What good is a technology or system if its intended users are unable to make sense of that technology? Information Technology aims to bring the system & user relationships closer together to solve meaningful problems.
Most education for IT is focused on the impact it has on th business but IT education is just as important for the home as it is for the workplace. Below are a few core topics in IT and how they relate to your home devices & network.
In IT, hardware refers to the physical elements that make up an information system, such as a computer, printer, keyboard or mobile device. Most device hardware is embedded into the piece of equipment and can not be readily seen. This will be a short guide to dig into what makes up the most common IT device: the computer.
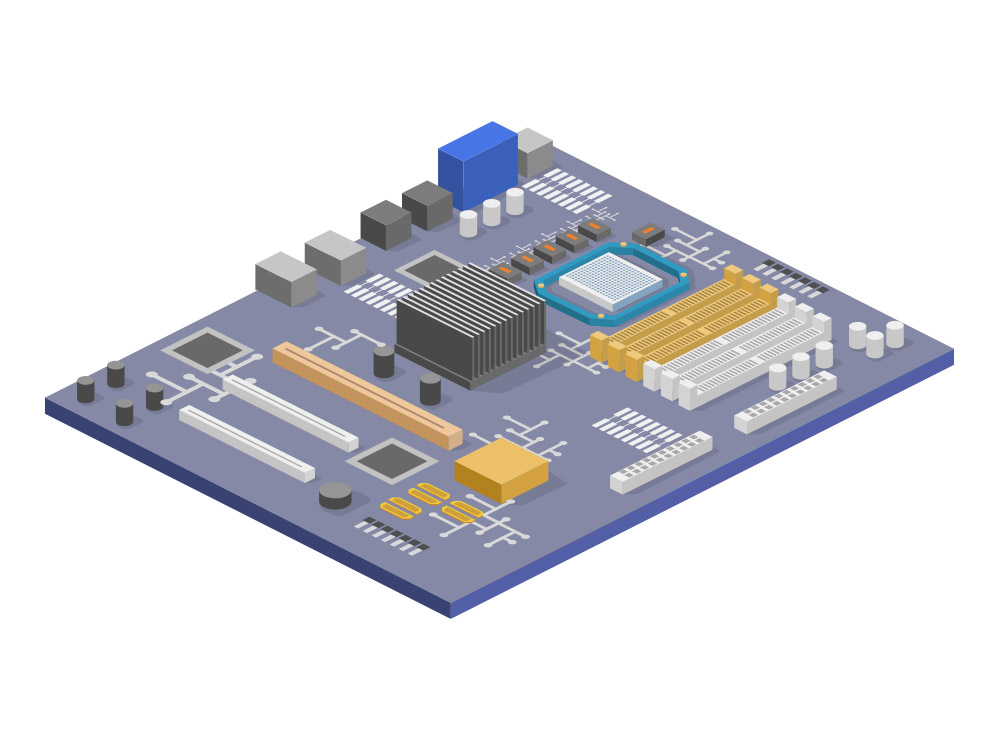
At the core of the PC is the motherboard. This powers and controls the device as well as connects other components to preform tasks or functions that the computer might not be directly able to perform. (ie. Motherboard contains a USB port to connect a printer to provide printing functionality o the device) Without the motherboard, none of the other device components would be able to communicate with each other. Motherboards come in a few common sizes for desktops: ATX, Micro-ATX & Mini-ITX. Each size has advantageous & tradeoffs that have to be weighed. (ie. Mini-ITX are the smallest size and might save space but sacrifices multiple PCI slots)

If the motherboard powers and controls the device, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of the operation. The CPU processes instructions that come from programs, operating systems or other components in your computer. The CPU is installed on the motherboard (called a socket) and needs a dedicated cooling component to keep temperatures under control during high processing demands.
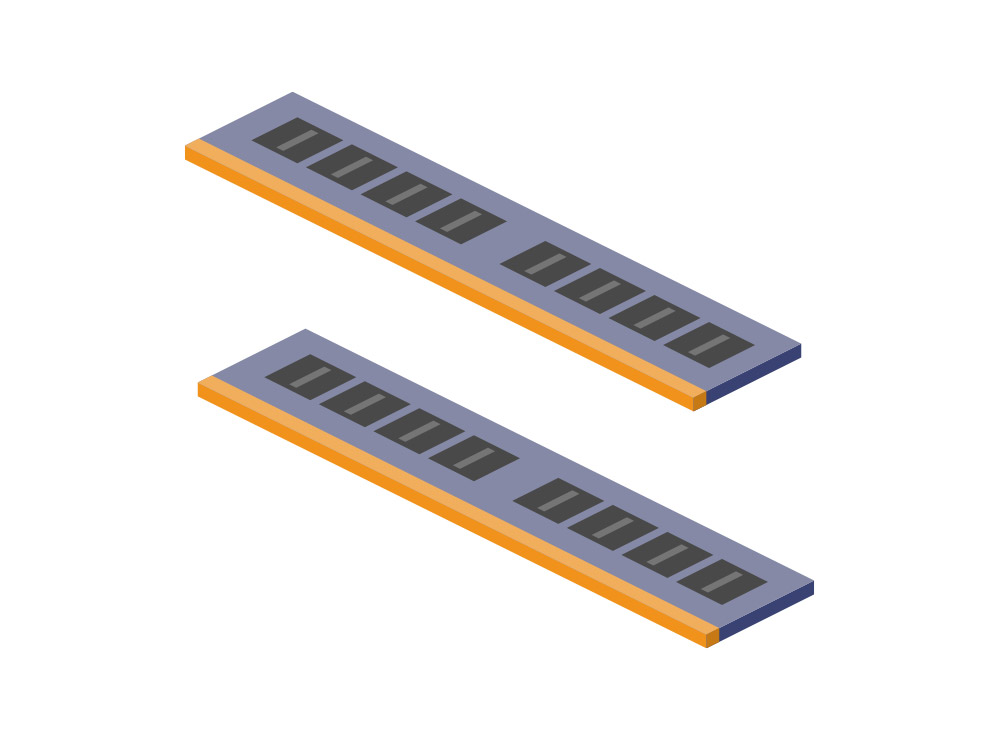
RAM or Random-access memory is memory that can be read and written in any order. It is used in storing temporary information used while your computer is operational. The more programs and services running on your computer, the more RAM storage is utilized. In older computers, upgrading the RAM can be a cost effective way of increasing the performance of your PC. While RAM helps handle temporary storage for the running of applications, once the computer is powered off, that information will not be available as it is cleared on shutdown.
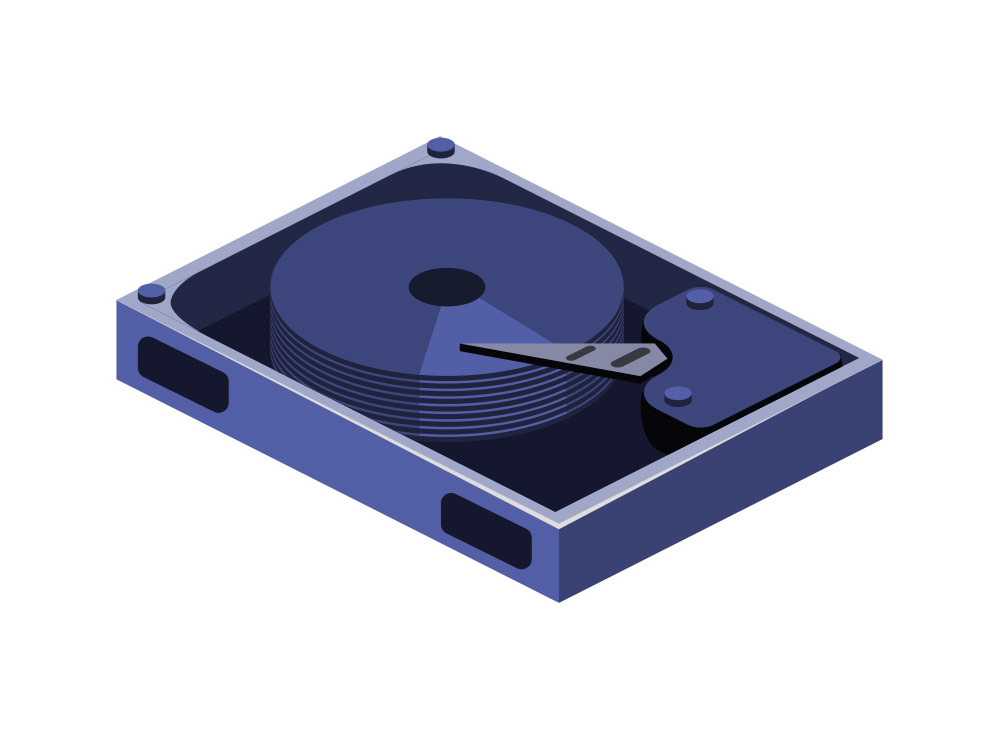
If RAM handles the temporary information needs of a computer, the hard drive handles the permanent storage of data in the PC. There are two main storage drive types: Hard Drives & Solid State Drives. Hard Drives are a common drive type, composed of metal disks that use magnetic storage technology (similar to tape decks) to store blocks of data. The data is retrieved with a stylus, very similar to a record player stylus and is transmitted to the motherboard. Given these types of drives are based on older technology, they are the most cost effective units for high capacity storage. Solid State Drives are a newer technology, composed of zero moving parts within the storage drive. This makes the speed at which data can be read, written & transmitted much faster as well as reduces the failure of the unit much lower than a spinning disk based hard drive. Storage drives have a few common sizes & connections: 3.5" SATA, 2.5" SATA, mSATA & M.2. Like the RAM component above, storage disks can be a cost effective way of upgrading the performance of your current computer.
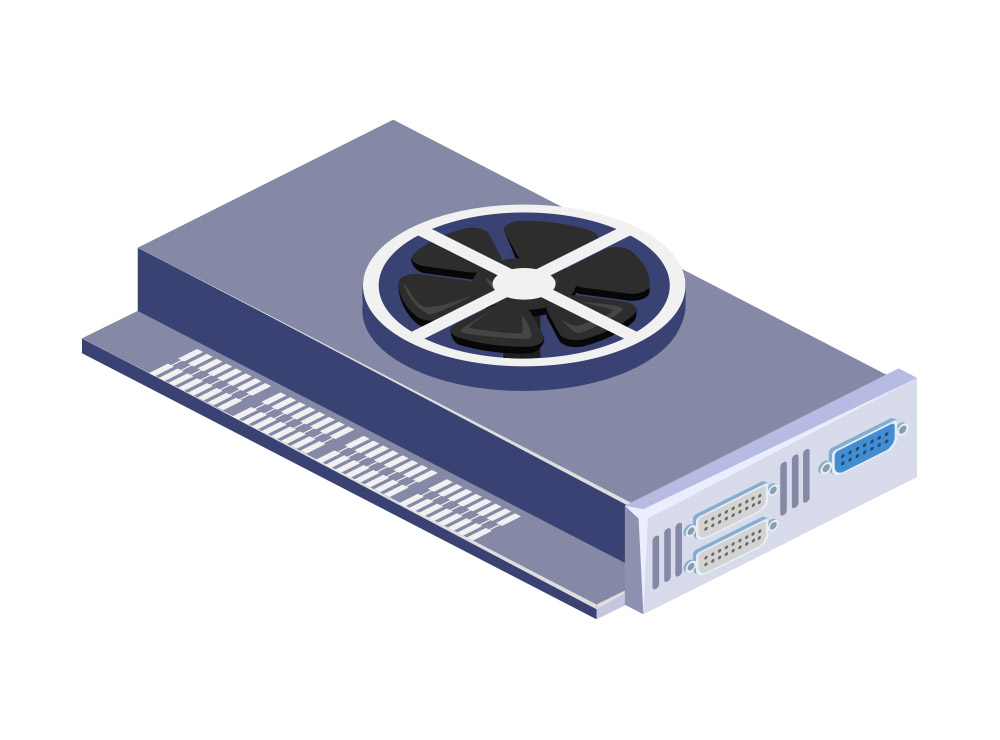

Your computer may or may not have a dedicated graphics processing unit but GPUs are an important component in modern computers as most computers now need to process graphics at a much higher rate than in the past. GPUs are great for processing images, 3D graphics & complex algorithm calculations and as such generally are the most expensive individual component in a PC. If you are looking to increase your graphics performance, purchasing a dedicated GPU will get you there.
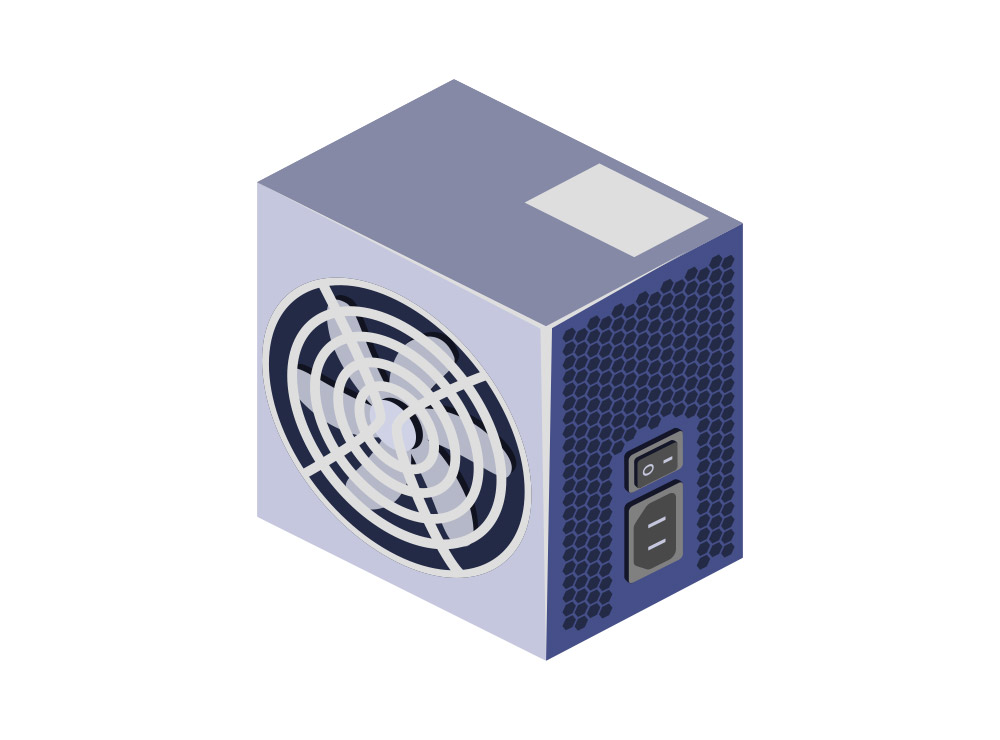

Power supply units (PSUs) are needed to convert AC voltage to a useable DC voltage that computer components need to power up and function correctly. In most common PCs, your PSU will be an ATX form size. When upgrading components in your computer, it might be necessary to upgrade your PSU in order to increase the power demand of that upgrade, this is especially true when upgrading your graphics card.
If hardware is the instrument of IT, software would be the tune the instrument plays. All software boils down to creating and managing the instructions your computer hardware needs to preform a specific task. Software can be broken into 4 main groups:
System software is the foundation for all other application software. System software can be operating systems, compilers, disk formatters, device drivers or system utilities. Different operating systems have different programming languages and structures, therefore some application software will only work with a specific operating system.
When users think of software, this is the type of software they think of. Application software will cover the majority of user tasks & functions such as productivity apps, data management, education or training, gaming applications & etc. Applications can be a single program or contain a collection of smaller programs.
Developers need tools to create software programs. These tools are grouped into programming software which can include debuggers, compilers, interpreters, text editors & shippers.
This software group is a group most user might not think of, however it is a group that warrants attention in order to avoid exposure to. Malicious software is a program or set of programs developed to damage or compromise other installed software. Malware can be direct or indirect in the damage they do. Examples of malware can be:
While a home network might not be as expansive or sophisticated as an enterprise data center network, the underlining foundations are the same. Networks are a collection of devices (nodes) that are connected together to share information (data). Home networks can be public facing, private facing networks or even both. Networks can share files, device capabilities (printer, speakers, etc) or software within that collection. Additionally they can be connected by cabling (wired) or radio frequencies (wireless). Concepts to be familiar with for all networks are:
A Media Access Control address is used to identify a unique device that connects to your network. All devices that can connect to a network will have a MAC address.
An IP address is a unique number assigned to every device connected to your network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Each IP address identifies the device’s host network and the location of the device on the network.
A node is a point inside a network that can receive, send, create, or store data. A few examples of nodes include computers, printers, modems, wireless access points, and switches.
A router is a device that sends information contained in data packets between networks. Routers forward data packets until they reach their destination node. The most common example of a router in your home network is the internet modem provided by your ISP.
A switch is a device that connects other devices and manages node-to-node communication within a network, ensuring data packets reach their ultimate destination. Your ISP can contain a network switch or sometimes this switch can be a separate device.
A port identifies a specific connection between network devices. Each port is identified by a number. If an IP address is comparable to the address of a hotel, then ports are the room numbers within that hotel. Specific application messages, processes & services run on different port numbers.
While the most common network cable types are ethernet cables, coaxial and fiber optic cables are used to connect networks together. Your ISP might bring in your internet service with a different cable than what the rest of your home network uses to connect with.
Home networks need to maintain a security first mindset just as much as enterprise networks do. A cybersecurity compromise is a compromise regardless of the network type or size. In most cases home networks might lack the resources an enterprise network has, such as active intrusion detection systems. This can lead to slower reaction times and could be harder to remediate the threat. Below are some best practices you can use on your home network
Whether the exploits and vulnerabilities you have been alerted to are widespread or not, conducting patching efforts as soon as you can is a sound practice to sustain. We recommend implementing a 30-60 day patch cycle for most networks. If you need additional support on creating a patching policy, or if you would like RLCS to provide a managed IT security first policy through one of our monthly IT support plans, let us know.
Highly skilled attackers do not create their attack chains overnight. As such, building your defense to only rely on the latest security patch for your home network is not a recommended approach. When RLCS creates a network, we implement layers of security parameters, such as on-premise firewall appliances with intrusion detection & prevention systems, end to end network traffic encryption, strict access control policies & security information and event management systems. This layered security approach provides the depth needed to today’s device & system interconnectivity.
As your connected device amount grows, your attack vector also changes. Maintaining a clear, up to date IT asset list for all devices is key to understanding what products might have exploits, with a particularly focus on internet-facing assets. RLCS can provide a home IT Risk Assessments with ITAM reports as a way to capture a security baseline for your home network.
We hope you find this Introduction to IT helpful. If you have any additional questions concerning these topics, or any other IT related questions please reach out to use at (904) 217-7504. For more education & workshops, visit our upcoming events page.